During the First World War the American 370th Infantry Regiment served by being integrated into French Army divisions, as were the other regiments of the AEF 93rd Division. The 370th Infantry was unique as the only African-American regiment then led by African-American officers.
Known as “The Black Devils,” the Doughboys of the 370th took part in the Oise-Aisne Offensive in autumn 1918, pursuing the retreating German Army until (and even after) the armistice took effect on November 11th.
The BFWWP is on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/BattlesoftheFirstWorldWarPodcast.
Any questions, comments or concerns please contact me through the website, www.firstworldwarpodcast.com. Follow us on Twitter at @WW1podcast, the Battles of the First World War Podcast page on FaceBook, and on Instagram at @WW1battlecast. Not into social media? Email me directly at verdunpodcast@gmail.com. Please consider reviewing the Battles of the First World War Podcast on iTunes.
*******
To get an idea of what patrons on Patreon get with every episode, this episode’s transcript will be posted in full here along with the accompanying maps. (You also get to see how I cheat by using photos of my sources so I don’t have to type every quote into my transcript. 😉
Many thanks to Dr. Jeff Gusky, who provided many of the photos below, and many merçis to Christophe Wilvers, who sent over photos of the former 370th sectors.
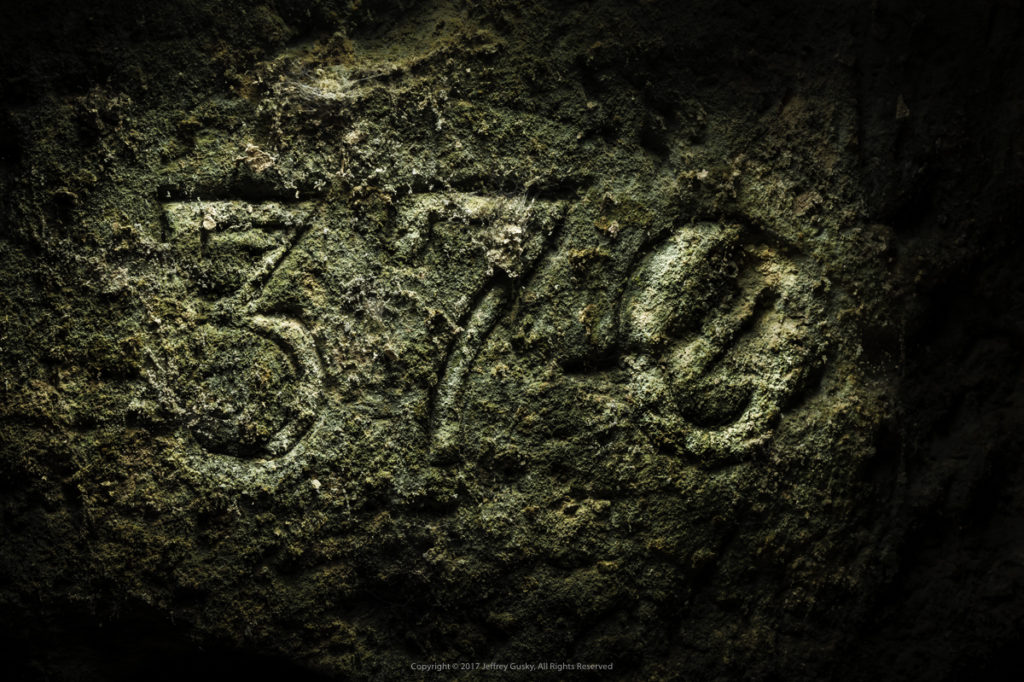
So, back to the front. This episode we will be rounding out our coverage of Black Americans in the AEF’s 93rd Division by looking at the experiences of the detached 370th Infantry Regiment. These Doughboys were attached to the French Army like their sister regiments of the 93rd, but they fought on the Oise-Aisne front. It may be a bit of a stretch here as the Oise-Aisne Offensive only supported the American-led Meuse-Argonne Offensive as much as the Meuse-Argonne Offensive supported the Oise-Aisne. That is, every Allied offensive in autumn 1918 supported the others because each one stressed the Germans’ reserves and forced them to retreat. But I didn’t want to leave the story of the Black Devils of the 370th untold.
As mentioned in Episode 64 “The 93rd Division in the Fight,” the 370th Infantry was a federalized Illinois National Guard unit, the 8th.
The 8th Illinois National Guard had a long and distinguished history by the time of America’s entry into the First World War, its most distinguishing asset being that in a time of institutionalized racism and segregation it was a regiment of Black Americans led by Black Americans. It was the only unit of its kind at the time. Its origins date back to the 1870s, and are occasionally tied to a non-state nor federally-sponsored militia group known as the Hannibal Guards.
The 8th Illinois was led by COL Franklin A. Denison, an attorney-turned-soldier who’d been the valedictorian in his class at Union College of Law in 1890 and made assistant prosecuting attorney for Chicago the following year. For a black man in that time, this was already extraordinary. Patriotic, Denison signed up for the 8th Illinois in the 1890s and later deployed with them to the Cuban theatre of the Spanish-American War. In postwar Cuba, Denison’s legal skills saw him become a military judge in Santiago. He stayed in the unit, and by 1914 was its commanding colonel.

Upon its arrival in France in April 1918, the 8th Illinois was federalized as the 370th Infantry and made part of the provisional AEF 93rd Division. As with the 93rd’s three other regiments, the 370th was handed off to the French, who gave it French equipment and then moved it to the St. Mihiel sector for live-fire training, which the opposing Germans were more than happy to provide. French military attachés and local nationals who saw them marching dubbed the men of the 370th “The Partridges,” as the soldiers proudly marched through French villages with a proud bearing and not a little bit of that cool swagger all young men have.
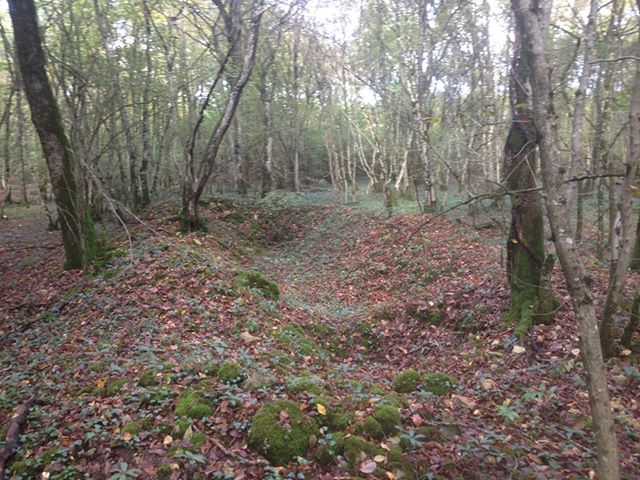
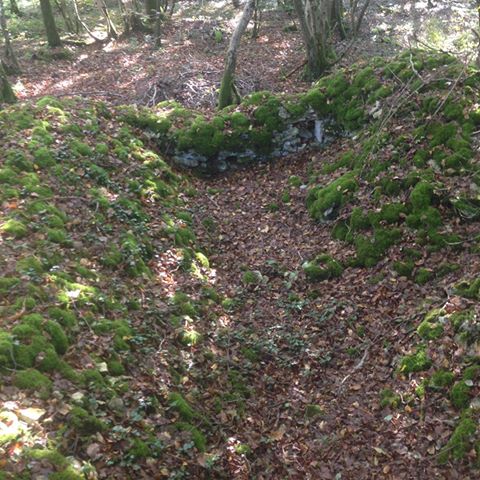
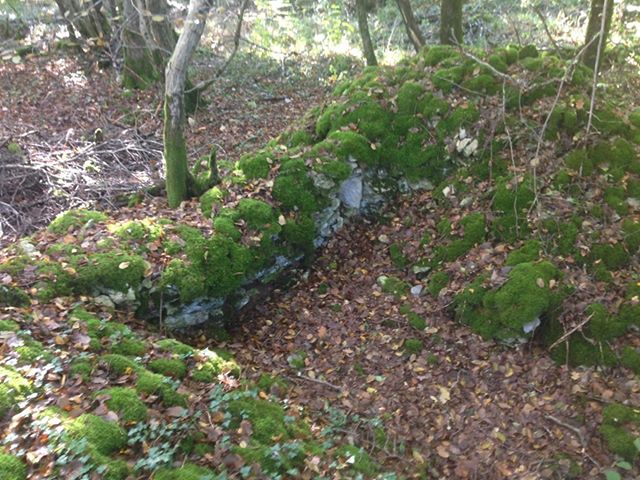
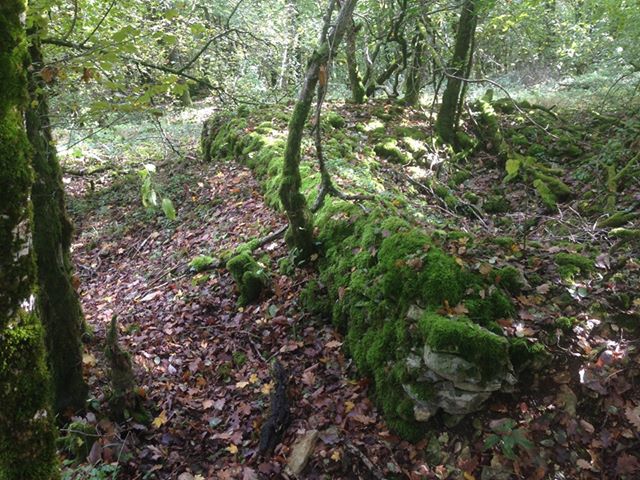
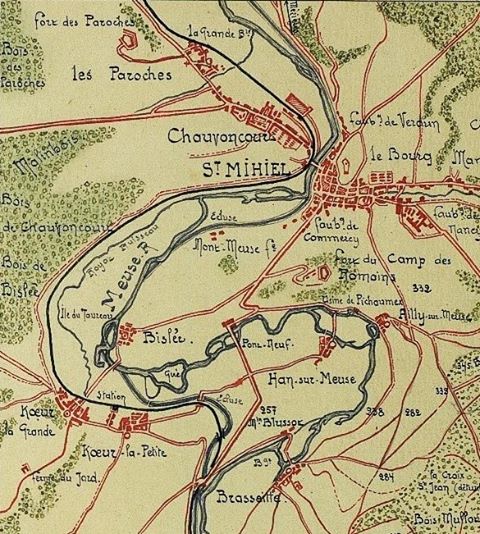
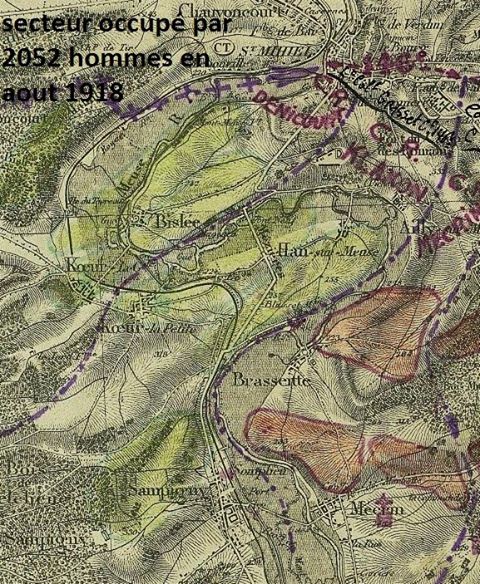
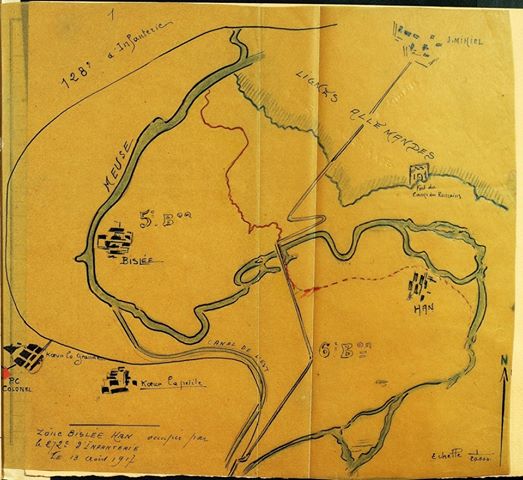







Coupled with the training regime however, the men of the 370th faced the same discrimination and racism the other black regiments of the American Expeditionary Force faced. Even under the wing of the French Army, the troops of the 8th Illinois still found themselves being used often for hard labor: clearing roads, digging and maintaining trench lines, and other grunt work. The 370th Infantry was an African-American unit commanded by African-American officers. In this era of American history, institutionalized racism was the order of the day, and it is likely that more than one entity or group was not keen on seeing such a unit succeed, nor its officers succeed.
As noted in Arthur Barbeau and Florette Henri’s work The Unknown Soldiers: African-American Troops in World War I, quote “[t]he 370th Regiment almost immediately began to lose its black officers, and the process continued throughout its war career. First to go was COL Dennison” end quote.
In June or early July, with orders to head for Chateau-Thierry, Dennison reportedly stated to the French 36th Infantry Division commander–to which the 370th was then attached–that due to recent training, quote “his men were not competent to take over a sector of such an important front, that they were neither American nor French soldiers, being in a transitory state; having been deprived of American equipment and without sufficient time to master the French equipment they were not half as good as an American or French soldier” end quote. CPT William S. Braddan, one of the chaplains for the 370th, confirmed this in his memoir titled Under Fire: With the 370th Infantry (8th ING) AEF; Memoirs of the World War.
In a June 1918 report, one US Army CPT George Marvin submitted reinforcing views on the performance of the 370th in theatre thus far. Marvin, an American liaison officer to the French, stated in his report that the 370th had failed in its training and deployment. It had failed in its training after the French instructors and their gear were switched out three times in three weeks, there was a war currently going on and at the time it was not going well for the French who were likely stressed out A-F by it all, and then the training was cut short and the 370th was put into the front line early by the French. And the Black officers didn’t speak French and had a hard time understanding the French Army’s supply system–where transactions were conducted in French. But yeah, the 370th had failed and quote “this regiment is unavailable for service at the front now and…will not be fit for two months to come, if ever” end quote.
Whether Dennison stated an uncomfortable truth whose honesty was not appreciated, or whether the politics of the day ruled, it was enough for the AEF command. The report was filed in the middle of June; on the 12th of July COL Dennison was relieved of his command on grounds of health concerns that disqualified him from front line service. He was sent home, and COL Thomas A. Roberts, a white officer, took command of the 370th.
Chaplain Braddan hated this new COL Roberts with the heat of a thousand suns, and this intense dislike springs from the pages of his memoir. Braddon’s memoir may not be objective as a result, but it is one of the few memoirs from the 370th available out there and it serves as a window into the world that was a century before our time. To the chaplain, COL Roberts, that quote “lantern-jawed coward” was the “arch enemy, vilifier, and traducer of the Negro soldier, the one who delighted to sign his private mail as coming from ‘The Great White Hope in a Black Regiment’” end quote. To Braddan, COL Roberts and the two white officers he brought with them were a sure sign that quote “it’s goodbye to all spade officers” end quote.
William Braddan had served for years with the 8th Illinois and was a tireless defender of the regiment. As a pastor of the Berean Baptist Church back in Chicago and thus a leader of the community, Braddan worked tirelessly to defend the achievements of the African-American community he served and lived in. Service in the 370th meant a lot to him, as he wrote in his memoir, and it is likely indicative of what the soldiers and officers of the 370th felt as well:
Quote “…After all these years of military service, I do feel that my duty is here for the present, to inspire and encourage this splendid group of men who have placed their bodies upon the nation’s altar, either for service or slaughter. I owe to my race this sacrifice, that I now gladly make, for I realize that upon the showing of this regiment (because of its entire personnel being Race men) depends the weal or woe of our race. If we fail, the race fails; if we succeed, the race succeeds. Knowing this as I do, I leave home, wife, children and a loving congregation for a season, believing that my race as a whole needs me more than loved ones at home.” End quote
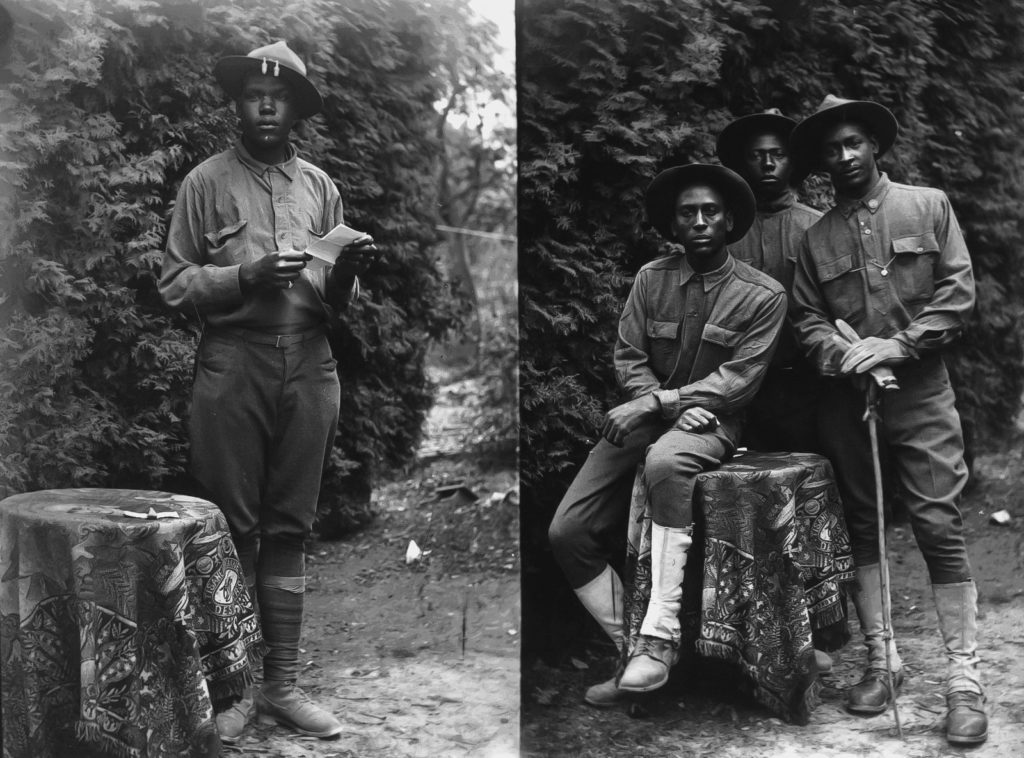

As African-Americans from the northern American city of Chicago, they still knew full well that racism and discrimination were never far away. The 8th Illinois Infantry was a beacon of achievement, progress, and hope for a better and more equal future for Black Americans. The men of the regiment were determined to serve their country and community well.
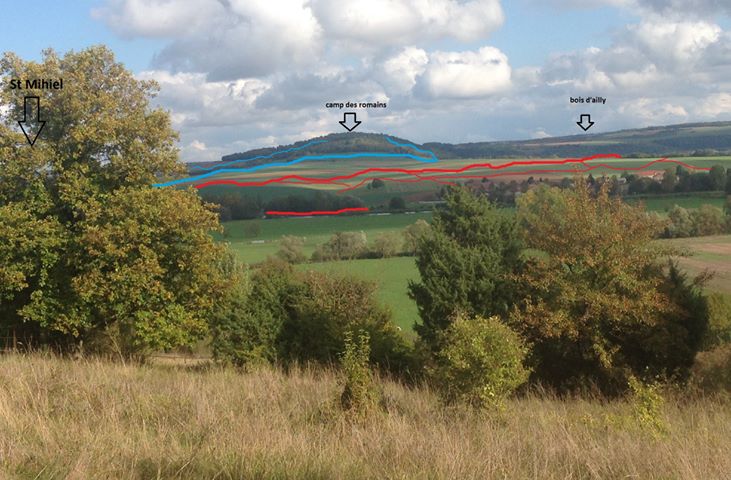
The regiment was transferred from the Lorraine area to the Oise-Aisne sector, where it was integrated into the French 59eme Division d’Infanterie–the 59th Infantry Division. In early September 1918, from lines north of Soissons, the French were steadily pushing the Germans back from the Marne salient, which had been stretched to its limit with the last of the great German offensives. First, the German line behind the River Vesle had been forced, and a retreat called. A new line was set up behind the River Aisne, and this was the new first line of the Hindenburg Line.
By mid-September the French 10th Army, under the leadership of that psychopathic tiger GEN Charles Mangin, was pushing towards the occupied city of Laon behind the Aisne. The River Oise-River Aisne canal line was to be cleared as part of this drive. Facing the French and American troops were the men of the German 7th Army.
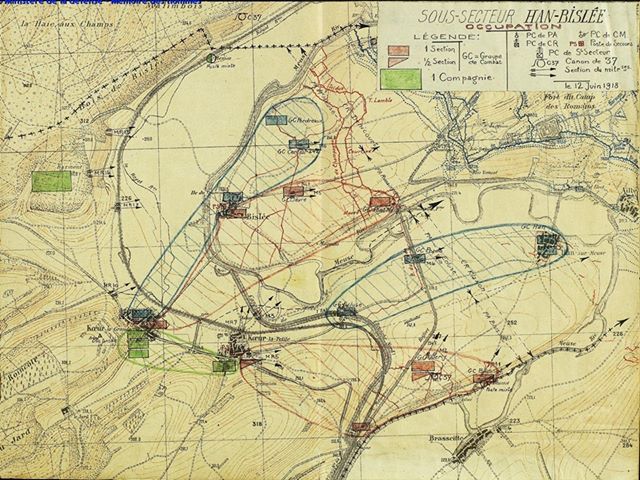
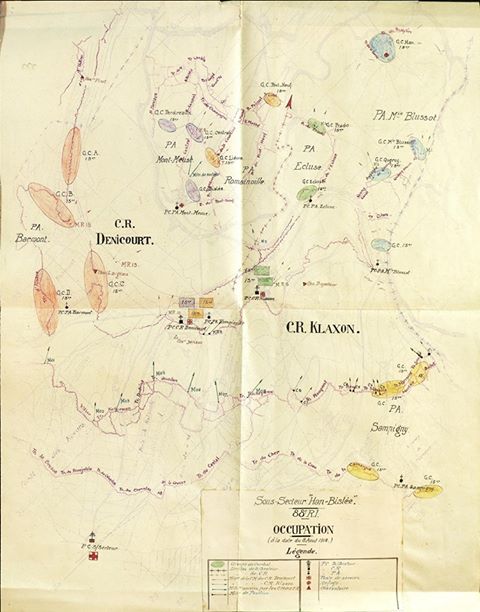
The French 59th Division was put into the line near the village of Vauxaillon, with the front running from the eastern edge of a wood named Bois de Mortier to the eastern edge of Moisy Farm. Moisy Farm sits SE of Vauxaillon, and directly north of it was Mont de Singe–Monkey Hill. Of this sector the French 232nd and 325th Regiments manned the line, with individual companies of the 370th split between them for support. This manner of breaking off companies piecemeal to be attached to French regiments is illustrative of why AEF commanding general John J Pershing had so adamantly stuck to his guns on maintaining his army’s independence. Pershing wanted to avoid his troops from being integrated this way into the French Army and the British Expeditionary Force.
On the 18th of September 1918, orders went out to clear German-occupied ground all the way to the Oise-Aisne Canal. Companies F, G, I, and L were part of the French assault forces. F & G Companies went with the French 232nd, and I & L went with the French 325th. Fighting on Mont de Singe was fierce, as the Germans were well-entrenched and had no intention of giving up the hill easily.
Fighting continued through the next two days, with the 19th seeing PFC Nathaniel White of Company F killed in action while running messages between command posts. PFC White was posthumously awarded the Distinguished Service Cross, an award second to the Medal of Honor, for his bravery under fire.
As combat raged across the French 59th DI’s sector, another Company F man made himself stand out for conspicuous bravery. SGT Mathew Jenkins was ordered to lead a 30-man group through No Man’s Land and link up with a French group laying low out there. The plan was for the combined groups to attack and seize the Hindenburg Cave, a local tunnel that served as one of the links in the enemy’s chain of fighting positions.
Jenkins lost men as they crossed open ground under heavy artillery fire, and when they reached the French he discovered that their own commander had been killed. A runner dispatched to the rear returned with a message for SGT Jenkins: take command of the entire group, and continue the mission. So here we have the rare case of a Black American NCO now preparing to lead both Black Doughboys and white Poilus into combat.
SGT Jenkins informed his new command of his plans, and then ordered that attack. Combat was short, sharp, and fierce, but the Germans were sent packing and the tunnel was seized. Then the Germans moved into No Man’s Land, cutting off the Franco-American force. The Germans began counterattacking. Remaining quick on his feet, SGT Jenkins set up a defensive perimeter that shot down successive counter attacks until ammunition ran out. But the tunnel yielded nearly a dozen and a half German machine guns with plenty of ammunition stored away; these were now turned on their former owners. For the next day and a half SGT Jenkins led the defense of his surrounded position, fighting off all German attempts to capture it. He and his men did so with no food and only German ammunition left for the captured machine guns. On the evening of the 22nd, SGT Jenkins and the remnants of his men and the French were relieved by a fresh French regiment. Jenkins would be awarded the Distinguished Service Cross for this action as well as for having previously rescued a wounded comrade under heavy fire before the tunnel defense.
CPT Braddan states in his memoir that following SGT Jenkins’ relief, he approached COL Roberts with the question, “COL, what do you think of my boys?”
“‘Not much,’ was the quick reply.”
“‘Why?’”
“‘Well, they are not making good.’”
“‘What do you mean, COL?’”
“‘Well, they failed to gain their objective yesterday and GEN Vincendon is very much disappointed.’”
“I don’t see why he should be disappointed,” Braddan replied firmly, “the men fought two days on an empty stomach over a terrain that was new to them, amidst a hell of shelling and not a man took air.”
“Well, Chaplain, for your sake I hope the men will not prove a disappointment,” was the COL’s reply.
This exchange came, of course, in late September and shows COL Roberts as thoroughly looking down on his new command. What’s interesting is that in August, after being in charge of the 370th for a little over a month, Roberts had reported,
Quote “Please don’t think that after a month I am convinced that I have a world beater of a regiment–it hasn’t gone that far with me yet; but there is a lot of excellent material that is not doing as much for the cause as it is capable of doing; the men are willing and as apt in most ways as most troops that I have seen; the officers are generally good as far as I have been able to observe them…” end quote
Furthermore, COL Roberts learned enough about his regiment that he could recognize an unfair issue: the 370th was completely isolated from all other American units. He also noted that the other regiments of the 93rd were also scattered, and that this had to have an effect on morale.
“…If the idea takes root that the regiment will never belong anywhere all the good intentions in the world will not advance it beyond a certain point,” he reported to AEF command. The units of the 93rd needed to be reunited, given supporting French artillery, and then let loose on the battlefield as a full division, or else quote “the angel Gabriel would have his hands full in trying to make anything of them–the same would apply to a white outfit” end quote.
Roberts’ suggestion fell on deaf ears, as we know, but the observations above do not seem to correlate with that of someone who was out to see the regiment fail, as Chaplain Braddan believed. The COL’s comments related to the 370th’s performance supporting those French attacks seem like they came not from a racial point of view, but from the point of view of a Regular Army man of the hard-charging “offensive a outrance” type looking down on National Guardsmen. Roberts’ comments have echoes of GEN Pershing’s own relentless hounding of his officers for vigorous attacks pressed with no regard to losses.
On the 22nd, the four companies were returned to the 370th so that the regiment could take over a portion of the front from the Oise-Aisne Canal to the foot of Mont de Singe, which now lay largely in French hands. 1st and 2nd Battalions manned the line, and for the next four days the Germans shelled the entire line constantly with HE and gas. The heavy artillery fire was to mask the Germans’ preparations to withdraw.
On September 28th the Germans began pulling back, and here the next phase of the Oise-Aisne Offensive began. The 370th was ordered to take up the pursuit along with the rest of the 59th DI, which attacked in a northeasterly direction towards Laon. The 2nd Battalion saw its right flank held up by heavy resistance, but the left cleared a wood west of the Ferme de la Rivière. In the afternoon, the Black Doughboys were assigned to protect the left flank of the entire division as it went in and eliminated a German salient. By evening they were probing across the canal into the Bois de Mortier, a large tract of woods that would need to be cleared out as well.
The next few days saw fighting in a triangle of land created by the River Ailette and Oise-Aisne Canal, a railroad, and the Pinon-Brancourt road. This area of land was SE of the Bois de Mortier, on the southern side of the canal. The 370th also continued pushing patrols across the canal into the Bois de Mortier, probing German defenses there.
On the last day of September, the 370th attacked a German position across the canal at 0900. Per CPT Braddan, the original French orders stated the attack would be at 2100, but that COL Roberts dismissed the orders out of hand and ordered the attack twelve hours early. The attack failed, and a GEN Rondeau who had apparently held temporary command of the French 59th Division or was a member of it, wrote a damning report on the 370th.
Per Rondeau, the 370th was quote “useless in combat” and “barring the COL, Regular Officer (White) of the American Army, all units, battalions, companies and sections are commanded by black officers of pronounced inefficiency” end quote. GEN Rondeau went to call the junior officers “strap-wearers,” or porte-galons, which was some type of insult in French back then, and said they were all useless and militarily ignorant cowards. However, in The Unknown Soldiers Arthur Barbeau and Florette Henri point out that there was some enterprise louche (fishy business) about this report, because this GEN Rondeau was not in command of the 59th on that day.
This report was compounded by another report submitted by a US Army MAJ Fredendall who inspected the 370th in early October and gave the regiment similar bad marks. He did say that the enlisted soldiers were doing their job as ordered and that 400 men listed as MIA were not deserters but likely got lost on the battlefield. However, it was absolutely unconscionable that the black combat officers would lose their way as well on the battlefield, especially when attacking over unfamiliar terrain and while the Germans were trying their best to kill them in a hail of gunfire. And MAJ Fredendall, well, he himself had become lost on the battlefield while attached to the 370th.
But COL Roberts, though labeled an enemy by Chaplain Braddan, had stated to the French GEN Rondeau on September 24th that quote “for reasons of nationality it is
of the greatest importance to leave the command of the units to Negro officers” end quote, and that while “the regiment was not as efficient as the French regiments, a marked improvement was manifest as the operation progressed…” COL Roberts probably recognized that the issues he and the others were seeing on the battlefield corresponded back to a lack of realistic training, and that the 370th and just about every other American regiment in France had been necessarily rushed half-ready into combat.
If the officers of the 8th Illinois were so poor, then why would mortarman 2LT Rufus Jackson locate German machine gun nests by drawing fire to himself? Why would LT William Warfield single-handedly charge a German machine gun crew, kill them, and then bring back the captured machine gun? If junior leadership was so flawed, what would inspire CPT William Crawford to personally lead his company into a wall of enemy machine gun and shell fire? The leadership couldn’t be any worse than it was in other American units at the time. All three men mentioned above were later awarded the DSC for their actions.
As the first days of October turned into the first weeks, the French 59th Division’s lines remained largely static. Short but incredibly violent artillery bombardments preceded vicious raids and counter attacks along the River Ailette canal line. Frank Roberts’ book The American Foreign Legion provides us an eye-witness account of one of these actions by a SGT Suesbury:
That morning was October 12th, and indeed the 370th attacked into the Bois de Mortier. The wood was cleared out after sharp combat, and the men continued on the heels of the Germans, who were now steadily retreating.
The next day the entire French 59th Division was relieved and sent rearwards for rest and refit. Over the next fourteen days the Doughboys of the 370th would spend twelve of them working as manual labor for the French. Despite GEN Rondeau’s claims of unpreparedness, the men of the 370th spent zero of those days in training.
On the 27th, the 59th was put back into the front line under the French 3rd Army, and the Illinois Guardsmen patrolled the new frontline in the vicinity of Cessières, well over 50km NE from the Oise-Aisne area. From here on out the war was one of steady movement, with the Germans giving the Doughboys hell but always giving ground.
On November 5th, the final pursuit began when the Germans withdrew from a village named St. Pierremont and the River Serre to the north and northeast of it. Combat was still the price to be paid for villages and important ground, but the Germans could no longer hold on. St. Pierremont fell and the advance was on. That night the Doughboys slept not in trenches but foxholes outside the village of Nampcelles. The war was now one of northeastward movement, albeit limited.
Three days later M Company under LT Osceola Brown was supporting a French company’s attack on a village named Logny, twenty-some kilometers NE of Nampcelles. The Poilus attacked as ordered but promptly found themselves under a horrific hurricane of machine gun and artillery fire. The Frenchmen pulled back even as LT Brown and his Doughboys got into their support positions, having braved the same artillery storm as the Poilus. Brown observed the village, and figured forwards was actually safer than rearwards back through the artillery raining down.
The LT ordered his men to attack the village, and the German defenders were shocked to be hit again so soon after just routing the French. Logny fell to the Americans, and Brown and several others would earn the Croix de Guerre from some no doubt rather chagrined Frenchmen.
The last three days of the war saw continued combat and staying in contact with the retreating enemy. German artillery fire remained heavy, and this slowed or stopped the relentless Allied advance at some points.
On the morning of November 11th, the advance continued on. There was word that there was to be a ceasefire at 11am that morning. The Black Devils of the 370th however, still had work to do. The war wasn’t over yet, and there was a German supply train of some fifty wagons with crews pulling back. The Doughboys set off after it, earning the Black Devils nickname given them by their French division commander. The Germans used the name as well, since these men wouldn’t let up.
As that fateful hour of 11am approached, the 370th troops continued their attack. The original objective had been a village named Regniowez, but as the morning went on the Americans pushed all the way towards Gué d’Hossus, a village on the Franco-Belgian border.
According to EJ Scott’s The American Negro in the World War, the armistice came and went, with the 370th still chasing after the German wagon train. They apparently caught up to it a half hour after the rest of Europe stopped fighting. This made them the last Black American unit in combat, and one of the last American units still fighting that morning.
With the capture of that supply train, the war was over for the 370th Infantry Regiment. While the Black Devils would not be awarded a unit Croix de Guerre, C Company was awarded one with palm for bravery. Seventy men were individually awarded the Croix de Guerre though, and twenty-one were awarded the United States Army’s second highest award for valor, the Distinguished Service Cross. While this record may not be on par with that of its sister regiment the 369th, it is still a record to be proud of.
In December of 1918, GEN Vincendon is said to have made statements regarding the 370th that refuted some of GEN Rondeau’s earlier complaints. Barbeau and Henri state that these comments may have been made in the euphoria of the immediate post-armistice timeframe, but again they do point out that the Black Devils had done their job and done it well.
“The 370th RI US,” GEN Vincendon wrote, “has contributed largely to the success of the 59th Division, and has taken in bitter strife both cannon and machine guns. Its units, fired by a noble ardor, got at times even beyond the objectives given them by higher command; they have always wished to be in the front line, for the place of honor is the leading rank. They have shown in our advance that they are worthy of being there.”
During its service on the Western Front, the 370th Infantry Regiment suffered 665 casualties, with 105 men killed or died of wounds. This put losses at around twenty percent of the regiment’s total. Adding the 370th’s losses to the rest of the 93rd Division’s casualties increased the losses there to around thirty percent of the total, which was only some 11,500 men to begin with.
To Chaplain Braddan, the service of his regiment also begged the question of where else they were worthy of being.
“…[T]he shades of night began to cover the torn and bleeding earth,” Braddan wrote in his memoir, “and hide the countless shell holes, bloated corpses of German and French soldiers who had crimsoned the daisies and made the poppies redder still, and with the coming of night came the flares, star shells and signal rockets from the trenches toward which we were going, crusaders of democracy, bearing that to the stricken French which we ourselves had never enjoyed in the land of the free and the home of the brave.”
“How often, Oh, how often in the days through which we passed over there, have I thought, how inconsistent for my government to send these swilling subjects to Europe to fight Autocracy, and for Democracy while it denied the same to its most loyal and patriotic subjects, the Negro. How unjust to send two hundred thousand Negroes three thousand miles to fight the Germans for destroying homes and killing the innocent, while at that very minute the members of the proud, powerful, enlightened and Christian American race were lynching, hanging and burning our brothers in America. I declare to God, no other race would have fought as fought the Negro in Europe, while at the same time the corpses of their brothers dangled at the end of a rope tied to a convenient tree or telegraph pole. Just and benign God, how much longer must my people endure in silence such treatment?”
